Medallion Architecture: A complete Guide
Medallion Architecture: understand Bronze, Silver, and Gold, best practices, governance, and how to scale data with quality
Jan 8, 2026
Medallion Architecture is a modern data organization pattern widely used in Data Warehouses, Data Lakes, and Lakehouses. Its goal is to structure data into progressive layers of quality, enabling better governance, reprocessing, scalability, and analytical consumption.
This model was popularized by Databricks and is now considered an essential best practice in modern data architectures.
What Is Medallion Architecture?
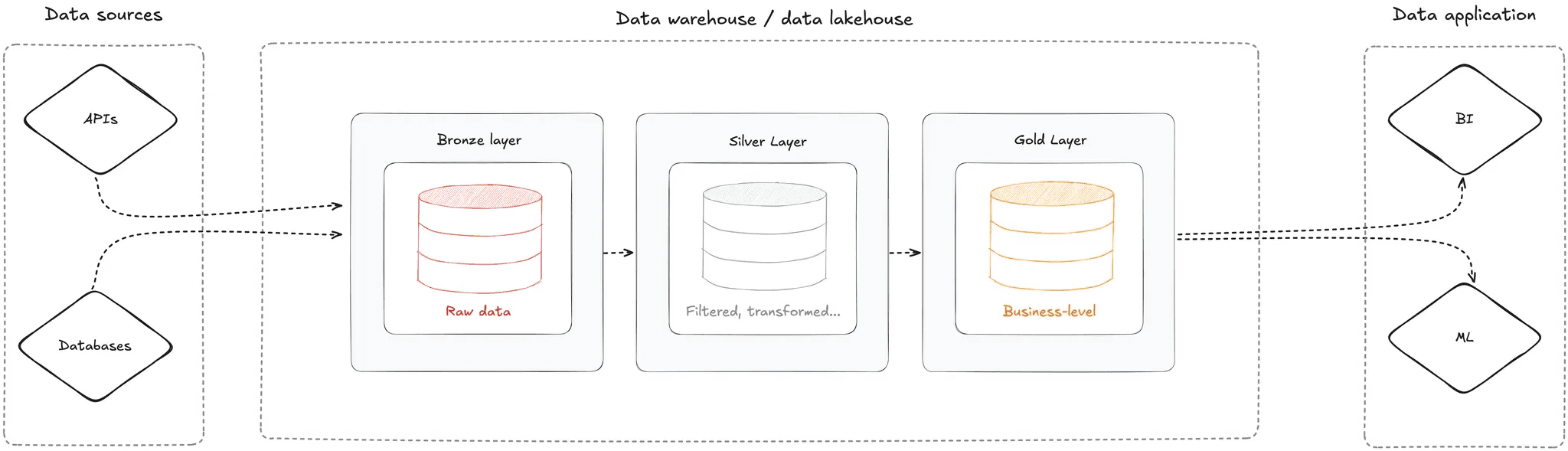
Medallion Architecture organizes data into three main layers, where each layer represents a higher level of refinement and value:
Bronze → raw data
Silver → cleaned and reliable data
Gold → business-ready data
Quick summary: data enters raw, gets cleaned, and is then transformed into business metrics.
Medallion Architecture Overview
Bronze Layer: Raw Data
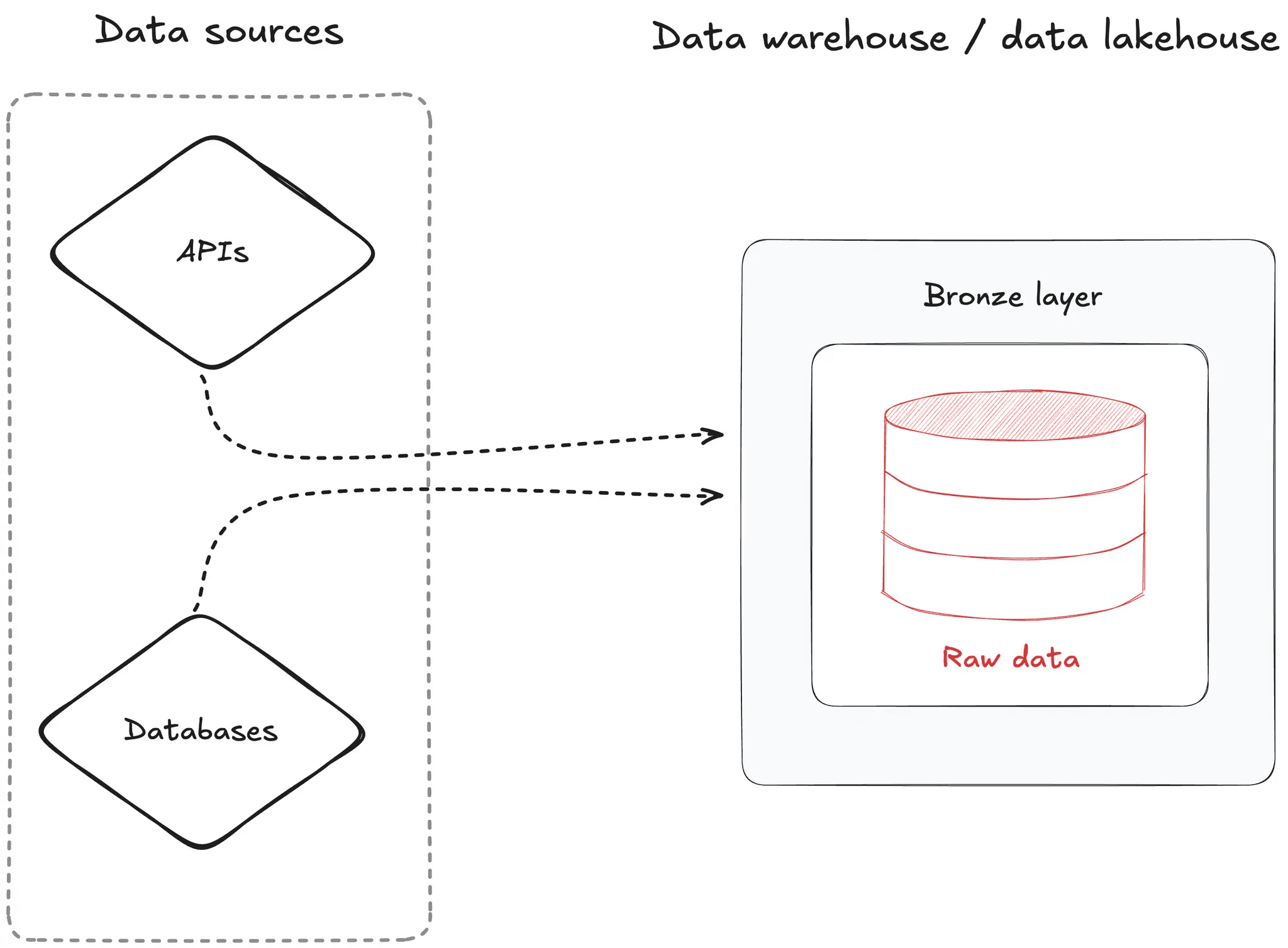
What is the Bronze layer?
The Bronze layer stores data exactly as it arrives from source systems, with no significant transformations applied.
Bronze layer characteristics:
Raw data
Structure close to the source
May contain errors and duplicates
High data volume
Foundation for auditing and reprocessing
🎯 Goal: preserve the original data as a single source of truth.
Silver Layer: Cleaned and Enriched Data
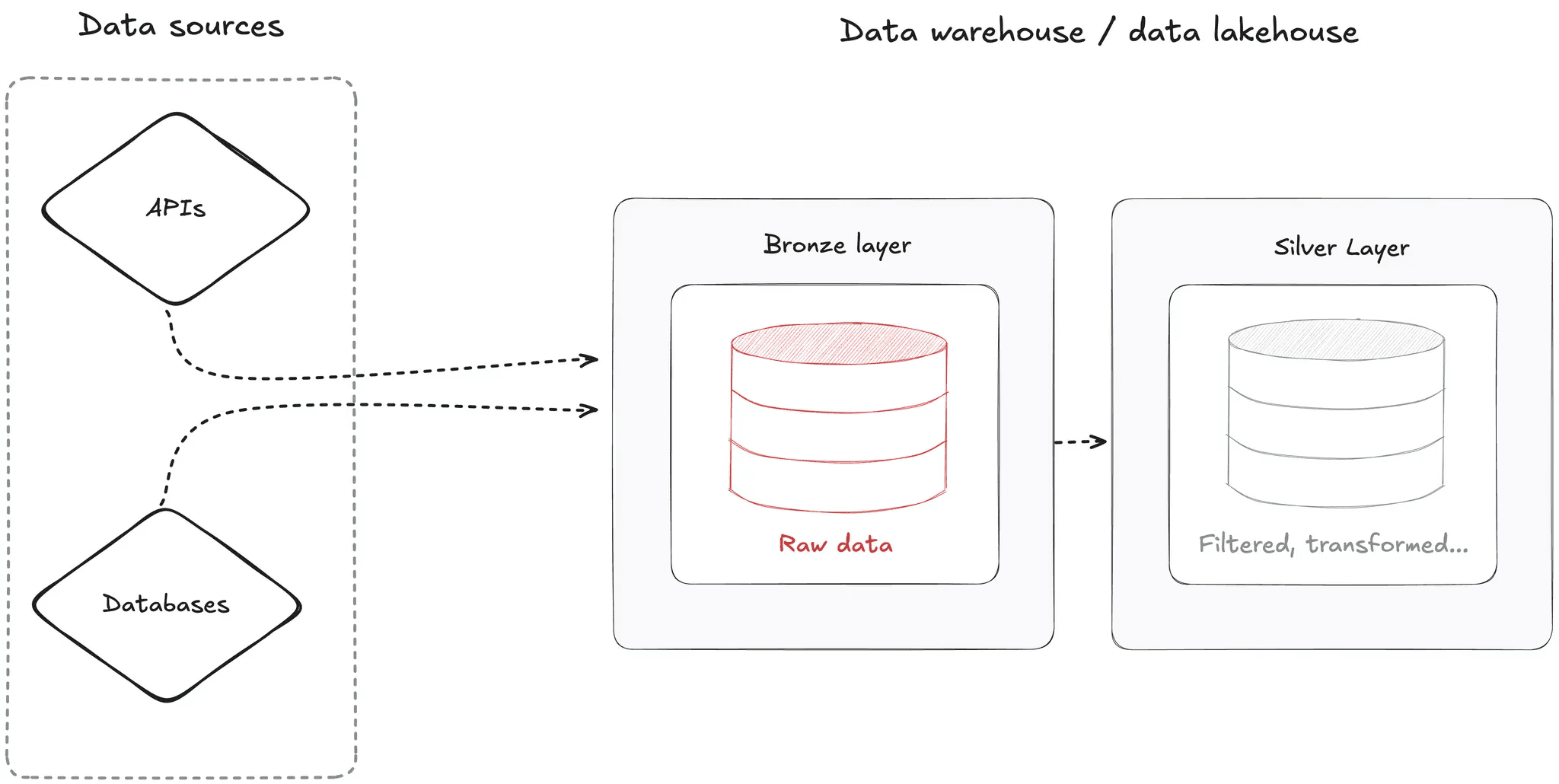
What is the Silver layer?
The Silver layer contains cleaned, standardized, and reliable data, ready for consistent analysis.
Common transformations:
Deduplication
Data type standardization
Mandatory field validation
Enrichment through joins
🎯 Goal: ensure data quality and consistency.
Gold Layer: Business Data (Business Layer)

What is the Gold layer?
The Gold layer represents the final stage of Medallion Architecture. At this level, data is ready for business consumption.
Examples of Gold data:
Monthly revenue
Churn rate
Lifetime Value (LTV)
Executive metrics
Goal: generate direct value for decision-making.
How Medallion Architecture Scales with Business Growth
One of the key advantages of Medallion Architecture is its ability to scale without requiring deep restructuring as the business evolves.
As new data sources are introduced:
They are ingested directly into the Bronze layer
Existing Silver and Gold models remain unaffected
Ingestion and consumption stay decoupled
This decoupling allows data teams to evolve pipelines and business models incrementally, without disrupting production reports or analytical products.
Medallion Architecture and the Evolution of Business Rules
Business rules change constantly: metric definitions, segmentation criteria, and financial calculations.
In Medallion Architecture:
The original data remains preserved in Bronze
Silver ensures structural consistency
Gold can be reprocessed whenever a business rule changes
This eliminates a common problem in traditional Data Warehouses: recalculating metrics without losing history or creating inconsistencies.
The result is greater trust in data and less reliance on manual fixes.
Governance and Observability in Medallion Architecture
The clear separation between Bronze, Silver, and Gold makes it easier to implement data governance and observability.
Each layer can have:
Different SLAs
Specific data quality rules
Independent monitoring
Additionally, issues remain localized:
Ingestion errors → Bronze
Data quality issues → Silver
Metric inconsistencies → Gold
This reduces troubleshooting time and improves overall data reliability.
Common Mistakes When Implementing Medallion Architecture
Despite its conceptual simplicity, some mistakes are common:
Applying business rules in the Bronze layer
Skipping the Silver layer to “move faster”
Creating multiple metric definitions in Gold
Not versioning transformations
Treating the architecture as a naming convention only
Avoiding these pitfalls is critical to achieving the full benefits of Medallion Architecture.
Benefits of Medallion Architecture
Improved data quality
Strong governance and traceability
Reliable reprocessing
Scalability
Clear separation of responsibilities
Best Practices for Medallion Architecture
Do not apply business rules in Bronze
Use columnar data formats
Version schemas by layer
Monitor data quality in Silver
Document metrics in Gold
When Should You Use Medallion Architecture?
Use Medallion Architecture when:
You have multiple data sources
Governance is critical
Reprocessing is frequent
Your Data Warehouse has become a bottleneck
BI and Analytics need to scale
FAQ – Medallion Architecture
What is Medallion Architecture?
Medallion Architecture is a data organization pattern based on layered data refinement (Bronze, Silver, and Gold) designed to improve data quality, governance, and scalability.
Can I consume data from the Silver layer?
Yes. The Silver layer is commonly used for exploratory analysis, data science, and advanced analytics, as it provides clean and reliable data without business-level aggregations.
Is Medallion Architecture only for Databricks?
No. While it was popularized by Databricks, Medallion Architecture is a conceptual architectural pattern and can be implemented using different technologies, tools, and cloud providers.
Does Medallion Architecture replace a Data Warehouse?
Not necessarily. Medallion Architecture often evolves and extends traditional Data Warehouses by adding clearer separation of concerns, better reprocessing capabilities, and support for modern analytics and machine learning workloads.
Conclusion
Medallion Architecture is one of the most important patterns in modern data architectures. By structuring data into progressive layers, it creates an environment that is reliable, scalable, and ready for growth.
If you are modernizing your Data Warehouse or building a Lakehouse, adopting Medallion Architecture is an essential step.
